Tools for Weigh the Whole Beef Meat
Meat & Poultry Fabrication
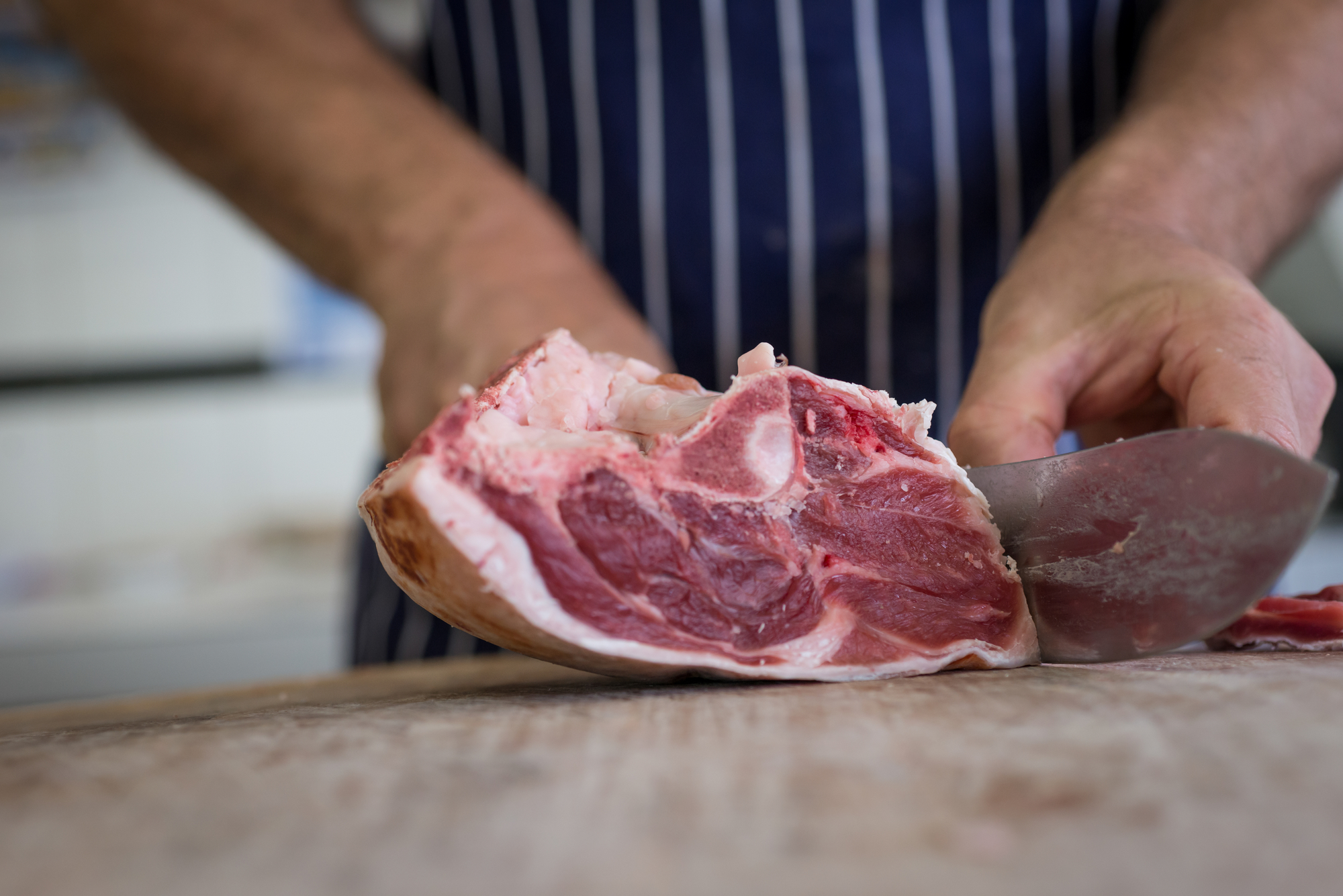

The extent of meat cut and fabrication performed in professional kitchens today depends on the philosophy and goals of the functioning. Some restaurants, because of the consistency and simplicity, adopt to purchase portion cuts. On the opposite end of the spectrum, some chefs today are adopting whole animal utilization and prefer purchasing carcasses or sides of meats to utilize in various carte applications. The success of a meat cutting program depends on quality command, nutrient toll control, and product utilization. It requires a knowledgeable person skilled at accurately cutting meats, poultry, fish, and shellfish, plus cooks defended to using not just the prime number cuts but under-utilized cuts, trim, and bone for other culinary applications.
Meat Fabrication
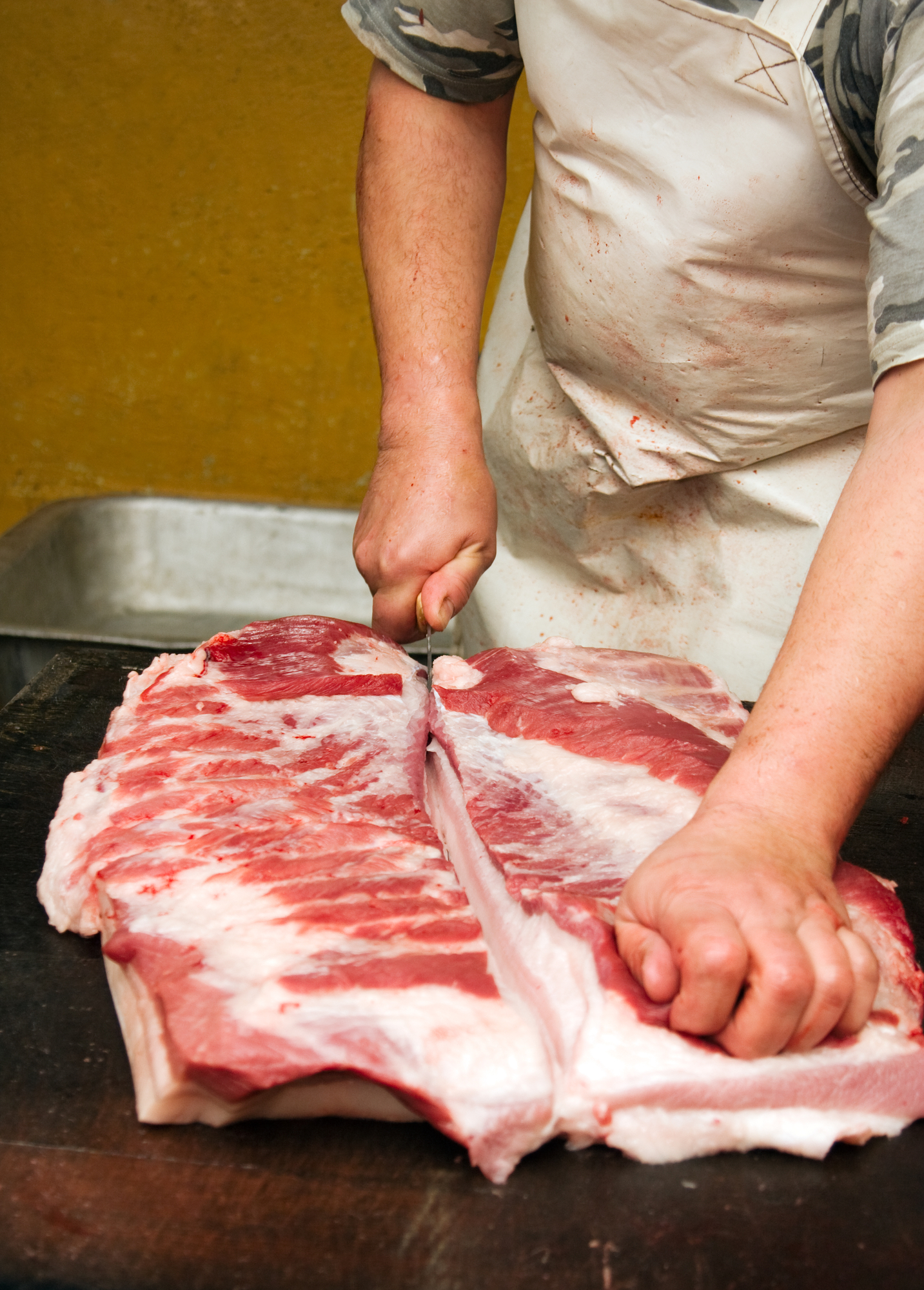

Butchering is a term commonly used for the procedure of slaughtering and preparing meat for retail or wholesale employ. Meat cutting, or fabrication , is the process of cut, boning, and portioning large cuts of meat to menu specifications. Becoming good at fabricating whole carcasses or primal meat cuts takes do often through an apprenticeship under a master meat cutter.
Dressed carcasses are processed whole , split into sides , or cut into quarters (fore quarter and hind quarter) . More frequently carcasses are made into primal cuts of meat. These are big cuts based on the muscle and bone structure of the brute. From at that place the meat is further divided into sub primal cuts that are often vacuum sealed and boxed fresh or frozen (the origin of the term "boxed meats") or the meats are processed farther into portion cuts as needed.
Skeletal and Muscle Construction
There are seven major bones in a skeleton that aid in meat identification and fabrication. Each of these seven bones are found in relation to one of the major muscles in the carcass (see skeletal meat chart).
Cardinal Cuts
There are four major cardinal cuts , the shoulder , rib , loin , and leg , constitute on all animal carcasses, but depending on the species in that location are some differences in naming and fabricating these cuts. For example, a beef chuck is the aforementioned cut as a lamb shoulder or pork shoulder barrel . A beef round is the same as a veal leg and a pork ham .

Location of the 7 Major Basic on a Beef Carcass
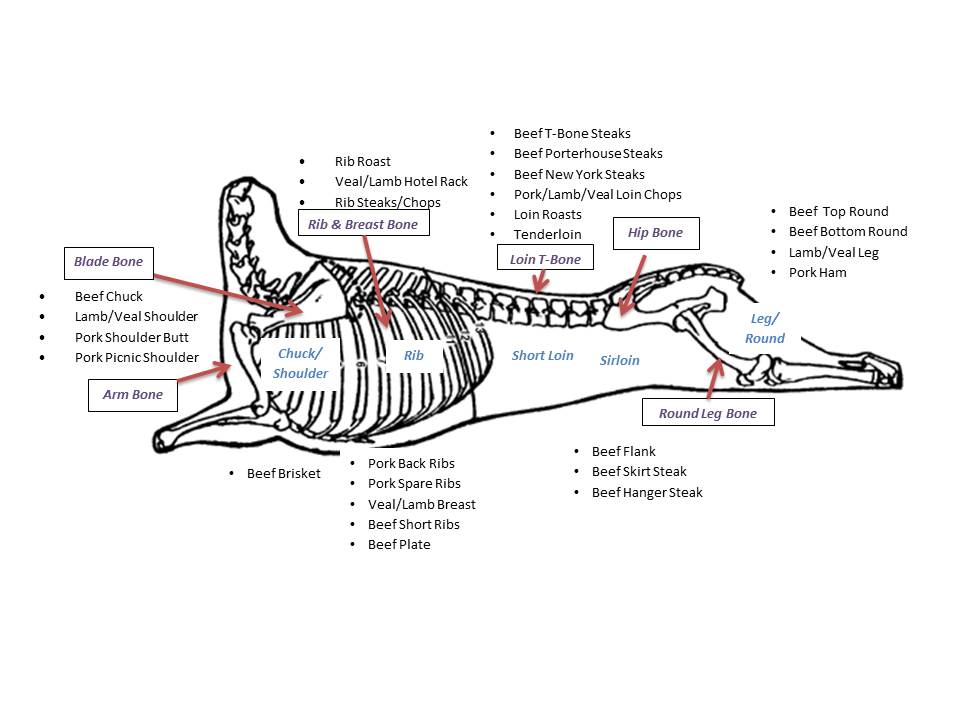
Sub-Central and Portion Cuts Derived from the Primal Cuts
Learning the advent and formation of major cuts along with the bones construction helps in fabricating as well as cooking. See specific meat charts on beefiness, veal, pork, and lamb for the names and locations of primal, sub primal, and portion cuts.
In that location are several minor primal cuts found on each type of carcass which are usually fabricated differently depending on the animal and its size. For instance, on a beef carcass the brisket , plate , and flank are separated into iii distinct cuts, simply on a veal carcass it is kept whole as a bone-in veal breast .

Lamb shanks and pork hocks (or shanks) are often cooked and served whole. Veal and beef shanks are usually cross-cut for braises or soups.
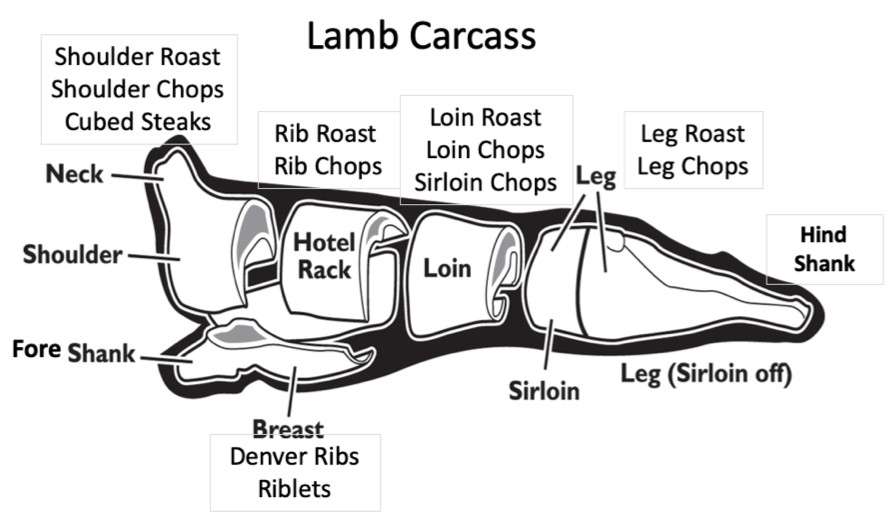
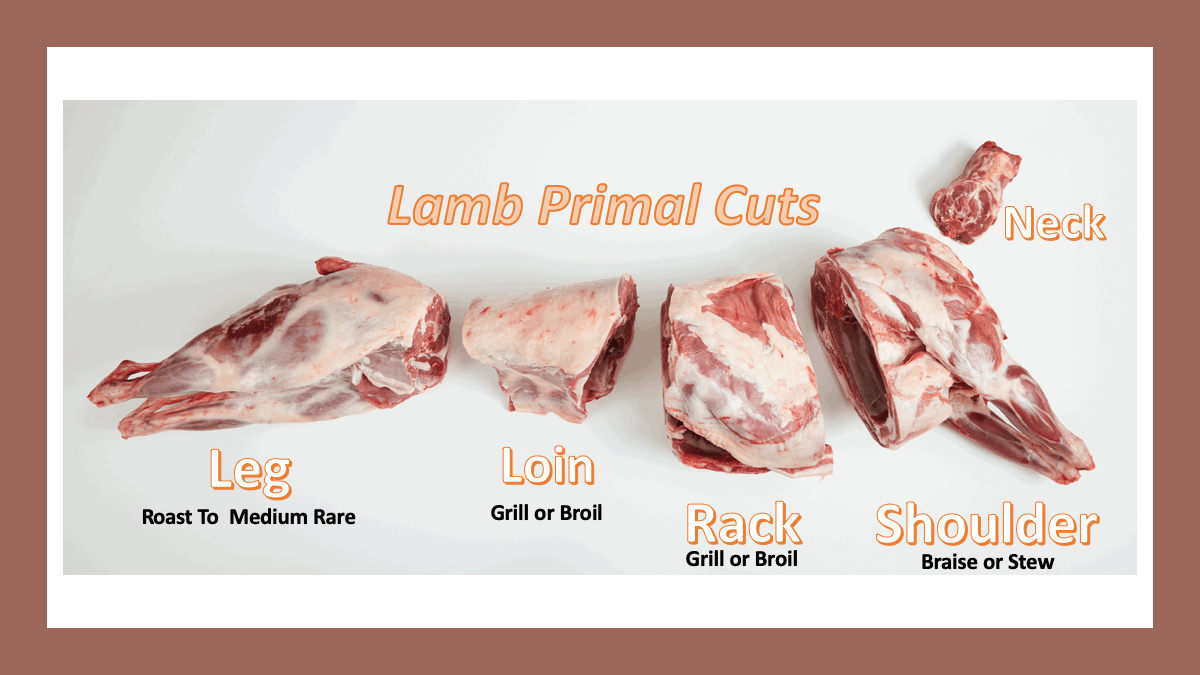
Everything Y'all Demand to Know About Lamb Fabrication
Pork carcass breakdown is notably different from beef, veal, and lamb. Whereas beef, veal and lamb split the rib and loin muscles between the 12th and 13th rib, pork carcass fabrication leaves this musculus intact and names it only the loin. Pork dorsum ribs are marketed for barbecuing. The pork belly is a much more prominent cut producing bacon and spare ribs . The pork shoulder is split into 2 cuts; the shoulder barrel and the picnic shoulder . The jowl produces a blazon of bacon, and the excessive fat ofttimes constitute along the behind of the beast is used every bit fatback or rendered for lard . The leg, known equally the ham , is often cured and sometimes smoked.
Fabrication Differences Based on Size
Size matters when fabricating meats. A beef carcass weighing in at 600 Lb./275 One thousand is about 33% larger than a veal carcass at 400 Lb./180 Grand . A pork carcass weighing approximately 270 Lb./125 G . is about 33% smaller than a veal carcass. A lamb carcass weighing nearly 65 Lb./30 Kg . is about one-quaternary the size of a pork carcass and one-tenth the size of a beefiness carcass. The yield on the same muscle from different species can exist dramatic. A steer tenderloin can weigh in excess of half dozen Lb./ii.7 1000, compared to a veal tenderloin at near 2 lb./900 g, and a pork loin at well-nigh 1 lb./500 thousand or a lamb tenderloin at a couple of ounces. Some viable cuts on a beef carcass such equally a hanger steak or flank steak are not marketable on a lamb or pork carcass given their small size.
Portion Cuts
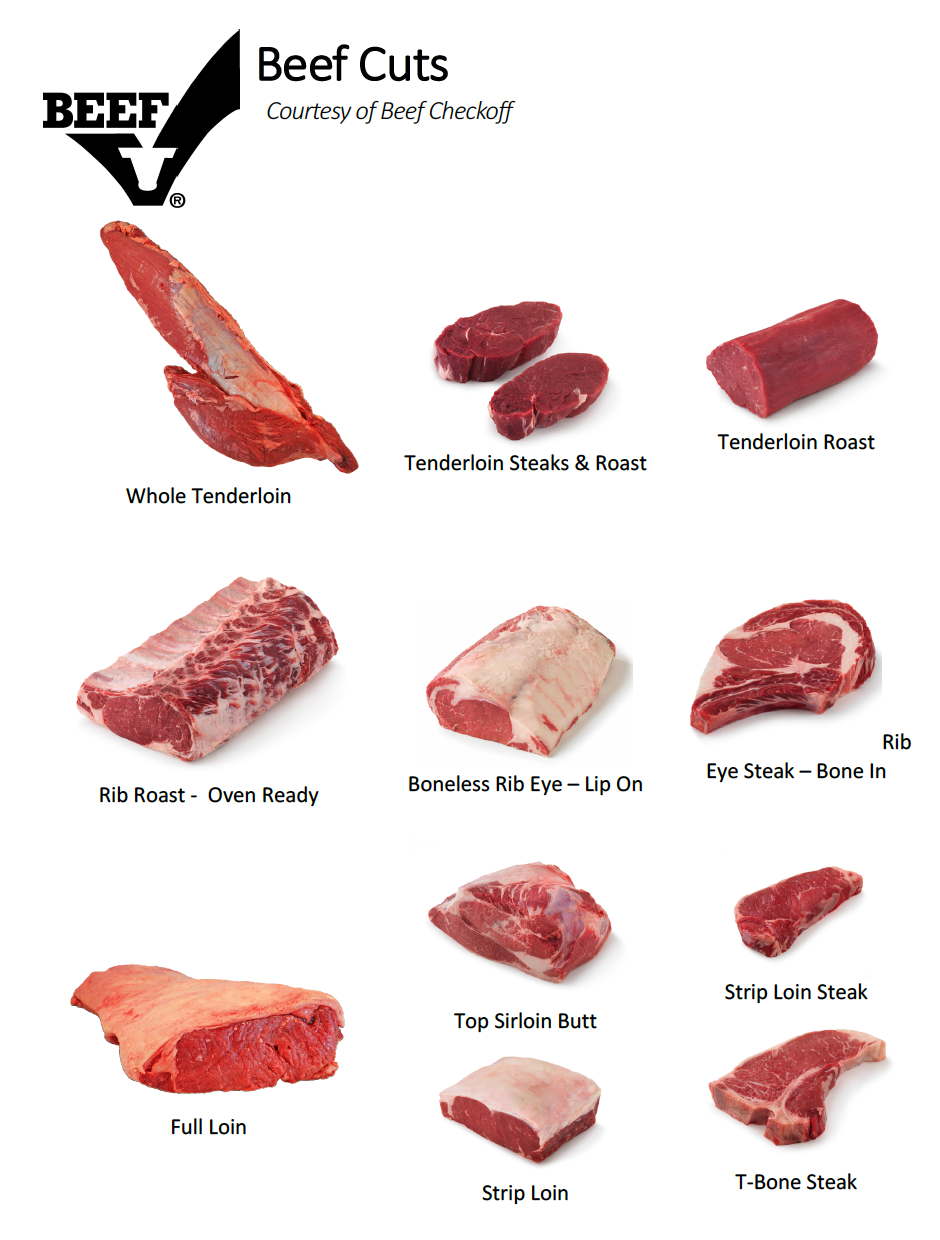
A beefiness full loin is an example of a primal cut. From the beefiness loin three major sub fundamental cuts are produced; the strip loin , the sirloin , and the tenderloin . A strip loin will yield New York strip steaks and if left on the os can be portion cutting into T-Bone and Porterhouse steaks . The tenderloin will yield filets , medallions , and tournedos . The sirloin yields elevation sirloin and beefiness culotte steaks. Each muscle eventually is portion cutting whether raw, or as in the example of a roast, later on cooking.
Commencement with a clean station and practice loftier standards of sanitation when cut meats. Keep the product common cold, and if needed place it on a pan of ice. Some operations will take temperature controlled rooms to go along the meats cold. Information technology'due south also of import to take the right tools that are properly sharpened and a honing steel handy.
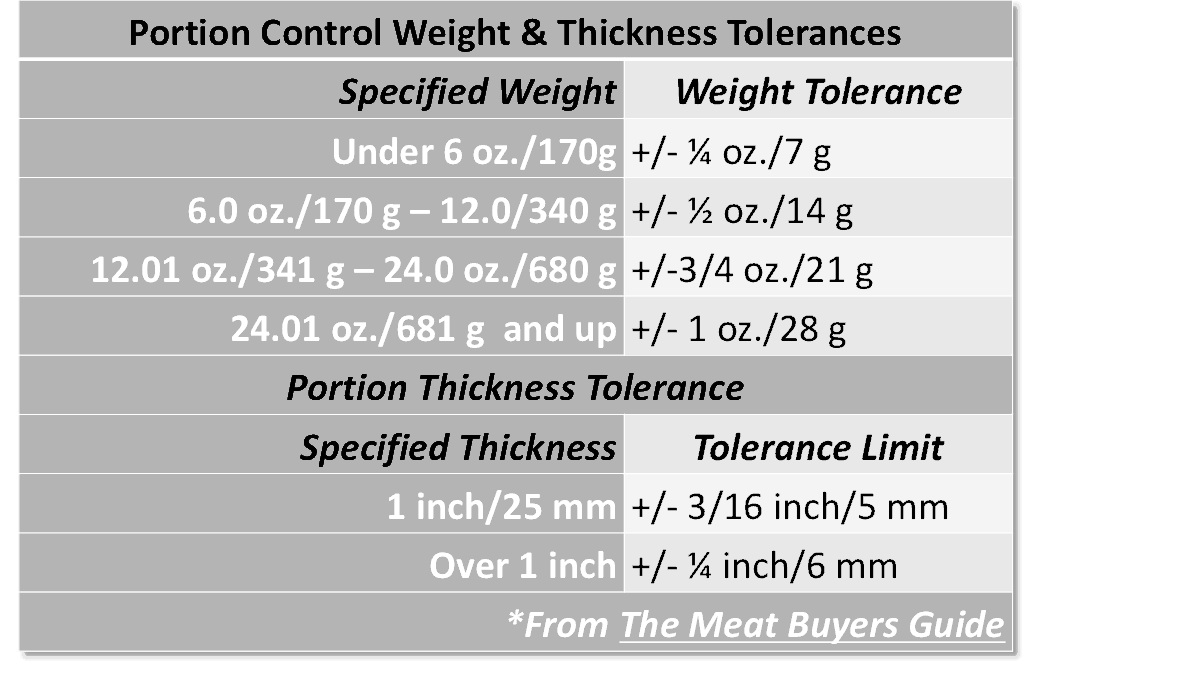
Portion Control
Meats are fabricated or ordered co-ordinate to the specifications of an operation based on portion size usually by weight and too at times based on thickness. These guidelines ensure uniformity in appearance and purchasing costs. Weight tolerance also helps to achieve consistency in quality from the perspective of customer satisfaction. The chart shows the generally accepted weight and thickness tolerance range according to The Meat Buyers Guide .
Cutting Management

Although whole muscles are fabricated without regard to the grain of the meat, portion cuts follow the general rule of cutting beyond the grain of the meat. This produces brusque fibers of meat that when served are easy to cut and chew.
While some cuts, like the loin and tenderloin, consist of whole muscles that are portioned by cutting across the grain, shoulder and leg cuts are made up of many muscles with varying degrees of tenderness running in different directions and making information technology more of a claiming to portion. For these cuts some muscles tin exist seamed out while others are too small and are used for braises, every bit stews, or for grinding.
Os-In or Boneless
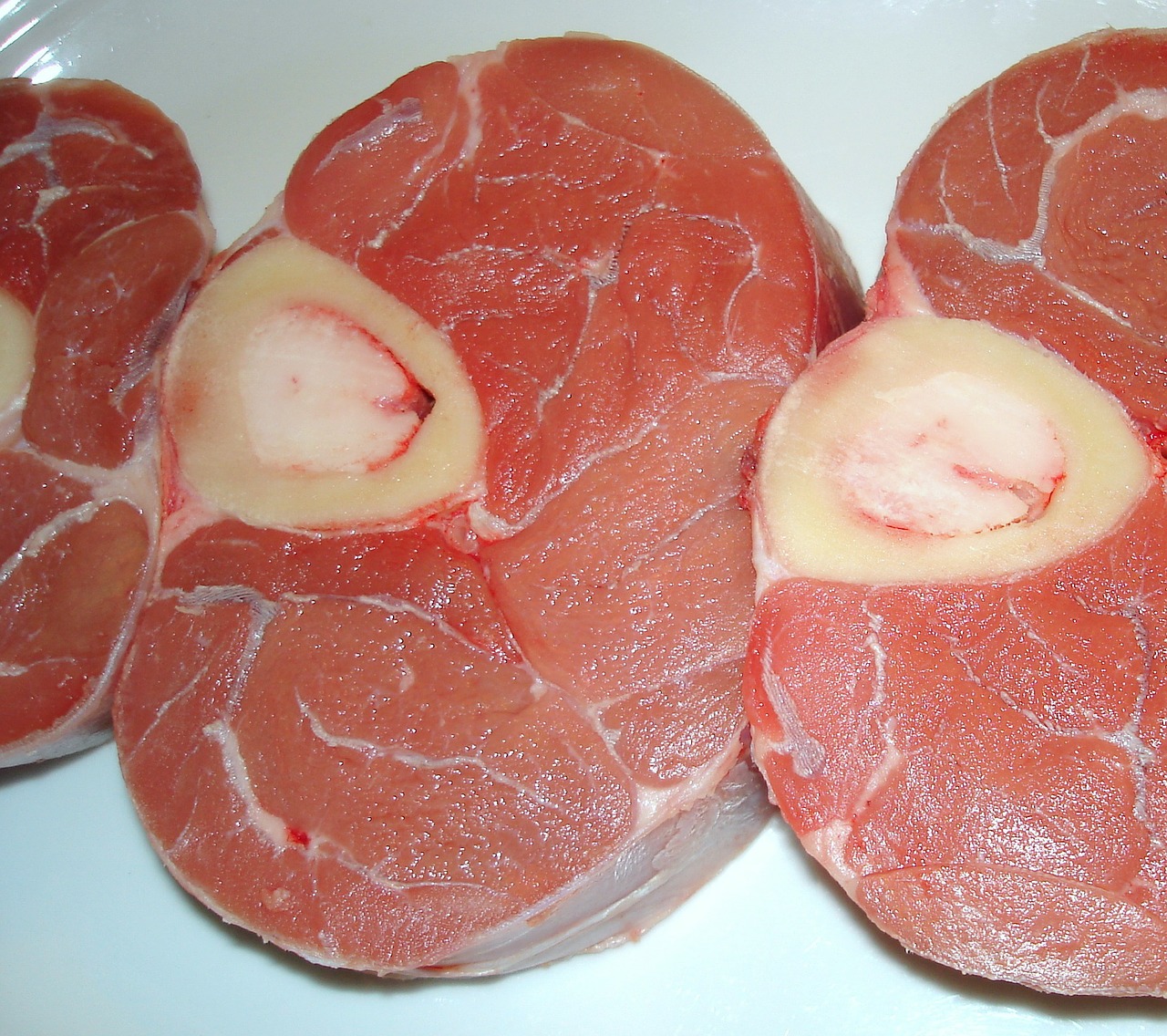

Cross-Cut Veal Shanks
Some cuts of meat, including T-Bone steaks, pork back ribs, rack of lamb, and shanks are fabricated os-in for appearance and flavor. Os-in meat will accept more than intense flavor upon cooking versus the boned variety. Today there is a preference in the United States for boneless meats that are like shooting fish in a barrel to consume without the demand to separaate the meat from the bone.
Connective Tissue
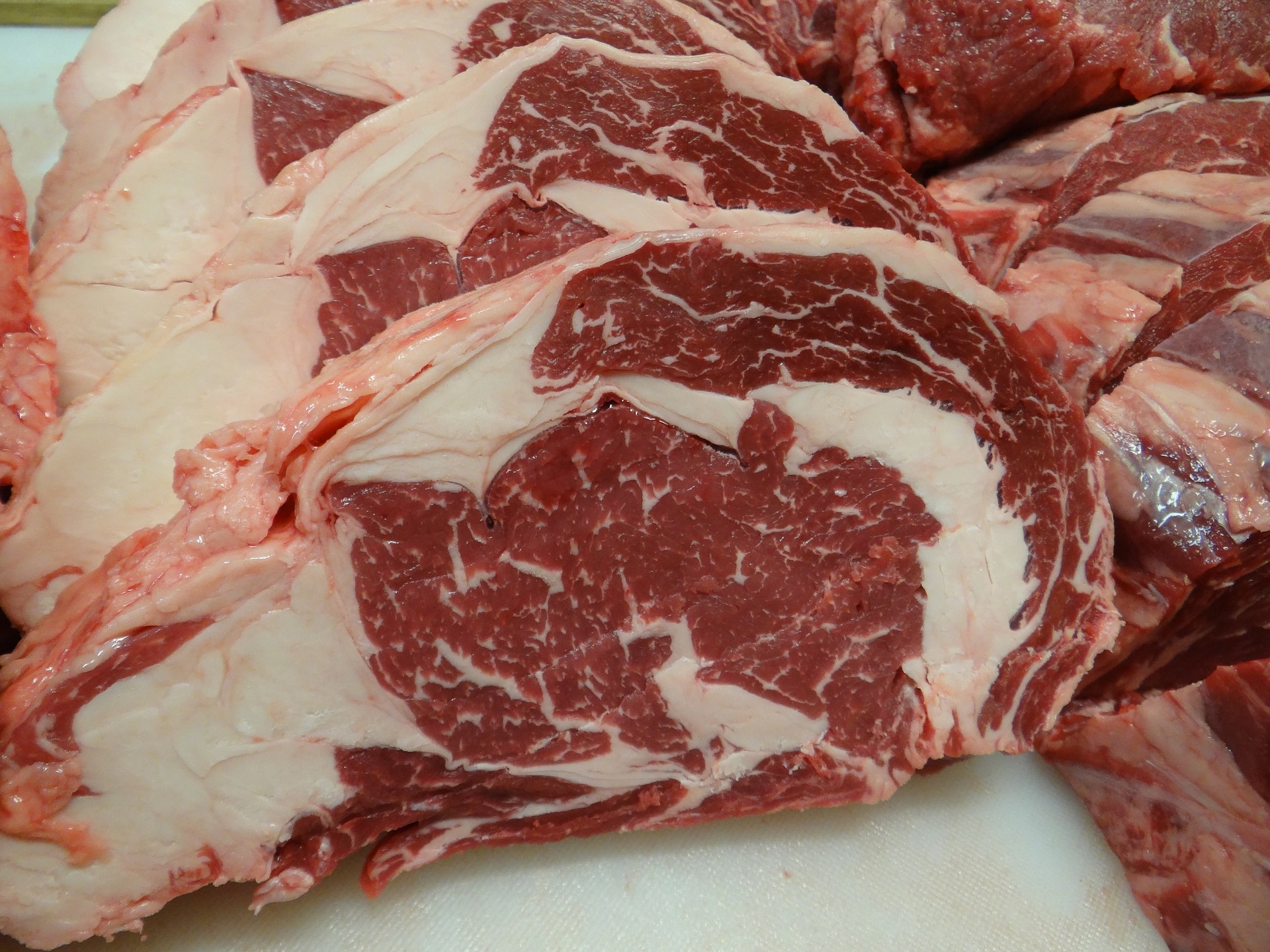

Connective tissue, found throughout the carcass in the form of elastin and collagen holds the musculus fibers together in bundles and also binds them to the skeletal structure. Elastin is tough and rubberband, as the name implies. Information technology does not break downwardly in the cooking process and therefore it is best removed. Collagen when heated melts and creates gelatin and is often left on the muscle for flavor and texture.
Fat
Cover fat and intramuscular fat in the form of marbling provides season and juiciness. When the marbling in meat muscles melts during the cooking process it provides flavor and juiciness. Comprehend fat on meat roasts baste the meat naturally while cooking when roasted fat side upwards. Removing cover fat or seam fat is necessary at times but considering it adds flavor care should exist taken not to remove as well much.


reyesmamrainy1941.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.theculinarypro.com/meat-and-poultry-fabrication-methods
Post a Comment for "Tools for Weigh the Whole Beef Meat"